The Future of Design: How AI is Transforming Creativity
Written on
Chapter 1: The AI Design Revolution
The landscape of design is rapidly changing as AI technologies emerge, allowing anyone to generate visual content. This shift raises important questions about the implications of AI-generated designs for creators and the broader design community.
Figma's AI Innovations
Using examples from Figma, we explore the significance of AI in design. AI can produce designs by assimilating established design systems—collections of guidelines, user flows, and libraries developed by designers over time. By analyzing these data points, AI learns to replicate effective design principles. Figma's recent "Make Designs" announcement sparked debate, but it reflects a broader trend among AI tools like v0.dev and KREA AI, which allow users to generate high-quality visuals by simply describing their needs.
Understanding 'Making Designs'
While websites and applications exhibit limitless variations, Figma has identified a handful of fundamental layouts that underpin most software. Familiarity with these patterns helps users navigate interfaces with ease, enabling AI to learn and replicate these foundational elements efficiently.
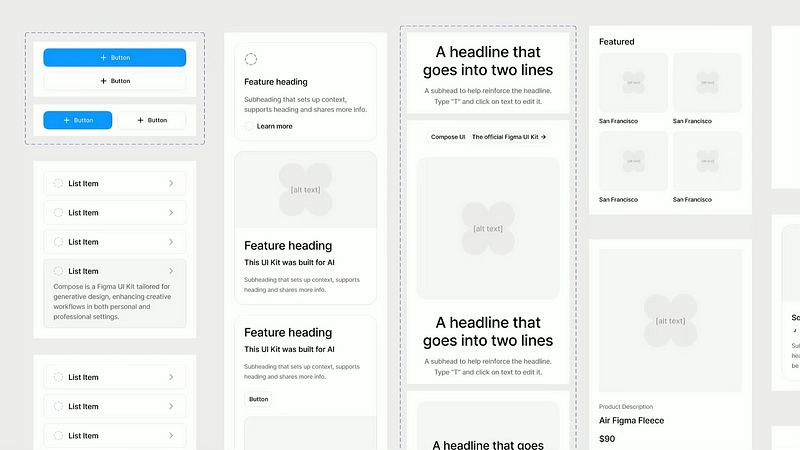
The democratization of design means that anyone can visualize concepts without needing artistic or coding expertise. This accessibility empowers designers to build upon a solid foundation, allowing them to concentrate on more complex creative endeavors.
Higher-Level Creative Endeavors
The distinction between computation and human craftsmanship lies in taste. While AI can endlessly reproduce designs from existing data, true creativity involves discerning and enhancing what makes something extraordinary. Although imitation serves as a valuable learning tool, exceptional design arises from unique perspectives and assumptions that cannot be simply replicated.
The Essence of Design
As Steve Jobs famously articulated, "Design is not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works." To design effectively, a deep understanding of the subject is essential; superficial enhancements cannot mask fundamental flaws. We can categorize design into three ascending levels: aesthetics, functionality, and product identity, where taste plays a crucial role.
Raising Standards in Design
Successful products often respond to user feedback, delivering exactly what users request. However, some groundbreaking designs introduce concepts that users never realized they needed, thereby shaping culture. High-quality design should feel so intuitive that it becomes second nature to users, as exemplified by the iPad's seamless integration into daily life.
The growing competition in enterprise products continues to elevate design standards. Effective design involves both responding to expressed user needs and recognizing unarticulated desires.
Designing with AI and Machine Learning
AI has the potential to revolutionize design processes, but realizing this potential poses challenges. While people often perceive AI models as possessing creativity, it is essential to remember that AI operates through mathematical algorithms. These models generate outputs based on existing data, which does not inherently reveal truth but rather informs decision-making.
Additionally, the application of general-purpose tools can be ambiguous, as their use can vary widely. For instance, a knife serves both culinary and potentially harmful purposes. Only through careful application can the optimal use of AI be demonstrated, with necessary safeguards.
As a primary distinction, AI yields unpredictable results. When users generate designs by clicking a button, they are essentially defining parameters for AI to operate within, creating guidelines for content generation.
The Future is Bespoke
User interfaces significantly influence our interactions with software. Software gains utility only when applied effectively. Currently, many AI-driven products are created by integrating numerous pre-trained models, which are then refined for specific tasks. For instance, AI can effectively design payment processes that have been established multiple times. However, it struggles with unique user experiences that require innovation and address novel challenges.
The future promises a personalized approach to AI, where individuals can tailor their experiences. Yet, design transcends merely producing visually appealing outputs. The goal is to elevate design standards, determining what constitutes excellence and ensuring the appropriate use of AI.
Exploring Further
For additional insights, hear from Noah Levin, VP of Design at Figma, on the evolving role of AI in design. The analysis presented in "The Guts of A New Machine" also offers valuable perspectives on how the iPod became a cultural phenomenon.
Related Articles:
Human vs. Machine: Framing the Right Problems for AI to Solve
Explore how successful AI products empower creativity by addressing the right challenges.
Intuitive Insights: The Evolution of AI Today
Understand why today's AI differs from its predecessors and the implications for design.
Why Do AI Projects Fail?
Examine the six key reasons behind the high failure rate of AI initiatives.
Thanks for reading!
I welcome your thoughts. Elaine shares insights on design, AI, and emerging technology. Connect for more updates on LinkedIn.
Chapter 2: Insights from Industry Leaders
The first video, "5 Secrets to Frustration-Free Designing," offers valuable tips on optimizing the design process and enhancing creativity.
The second video, "How to Design a Clear Future Self Vision for Your Creative Life: 100 Day Project 2024 Progress Video," explores methods for envisioning and achieving your creative goals.